Diabetic foot disease is a serious condition that affects many individuals with diabetes, leading to ulcers, infections, and even amputations if not managed properly. Orthopedic treatment plays a critical role in preventing complications and promoting healing by managing infections, preserving tissue, and improving mobility. In this guide, we will explore how orthopedic care can significantly improve the outcomes of individuals suffering from diabetic foot disease, enhancing both recovery and quality of life.
What is Diabetic Foot Disease?
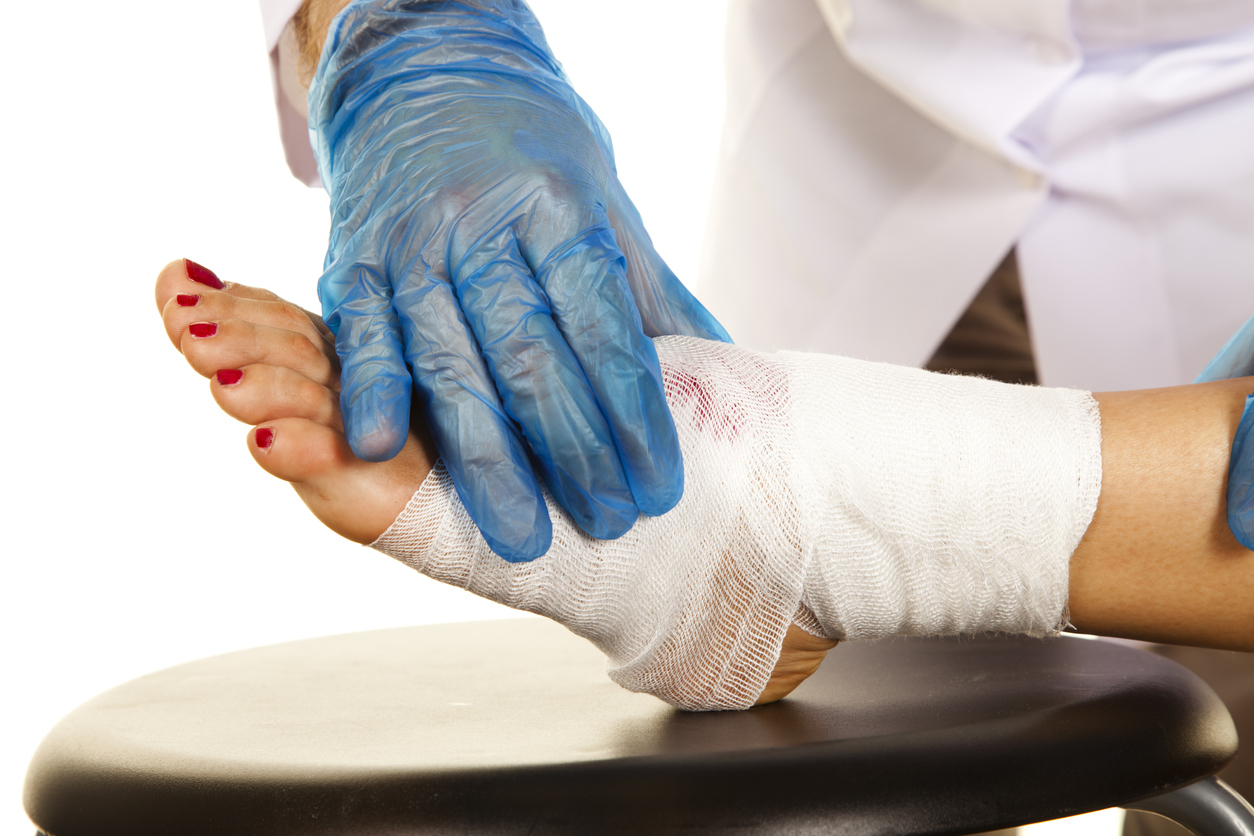
Diabetic foot disease refers to a collection of complications that occur in the feet as a result of uncontrolled diabetes. The most common issues include foot ulcers, infections, and poor circulation. These problems arise due to two primary factors: nerve damage (neuropathy) and reduced blood flow (peripheral artery disease).
When blood sugar levels remain high over time, it can damage the nerves, leading to numbness and loss of sensation in the feet. Additionally, poor circulation makes it harder for the body to heal wounds, increasing the risk of infection. Left untreated, diabetic foot disease can lead to severe complications, such as amputations.
How Diabetes Affects Your Feet: Understanding the Link
The link between diabetes and foot complications is primarily due to two factors: neuropathy and poor circulation. Neuropathy occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves, particularly in the feet, leading to a loss of sensation. This makes it difficult for individuals to feel cuts, blisters, or pressure sores, which can easily turn into serious infections.
Poor circulation, another consequence of diabetes, limits blood flow to the feet, hindering the body’s natural healing process. This combination of factors significantly increases the risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers and infections.
Common symptoms of diabetic foot disease include tingling or numbness in the feet, changes in skin color, swelling, or the development of blisters or open sores that don’t heal.
The Role of Orthopedic Treatment in Managing Diabetic Foot Disease
Orthopedic intervention is essential for managing diabetic foot disease, as it helps prevent complications such as infections, deformities, and amputations. Orthopedic specialists are trained to assess foot problems, diagnose conditions early, and create treatment plans that prioritize both healing and mobility.
Orthopedic treatment plays a crucial role in:
- Preventing infections through careful management and monitoring
- Preserving healthy tissue by addressing ulcers and sores
- Enhancing mobility with proper footwear and therapeutic interventions
In many cases, early intervention can prevent the need for more invasive treatments, such as surgery or amputation, by addressing issues in their early stages.
Key Orthopedic Treatment Options for Diabetic Foot Disease
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease varies depending on the severity of the condition. Below are some of the most common treatment options:
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
- Infection Management: If an infection is present, it is essential to manage it promptly with antibiotics and proper wound care. Orthopedic specialists often collaborate with podiatrists to clean and dress wounds, reducing the risk of further complications.
- Custom Footwear and Insoles: Specialized shoes or insoles can reduce pressure on problem areas, prevent ulcers from forming, and improve comfort and mobility. These are particularly helpful for individuals with deformities, such as hammertoes or Charcot foot, that affect the shape of the foot.
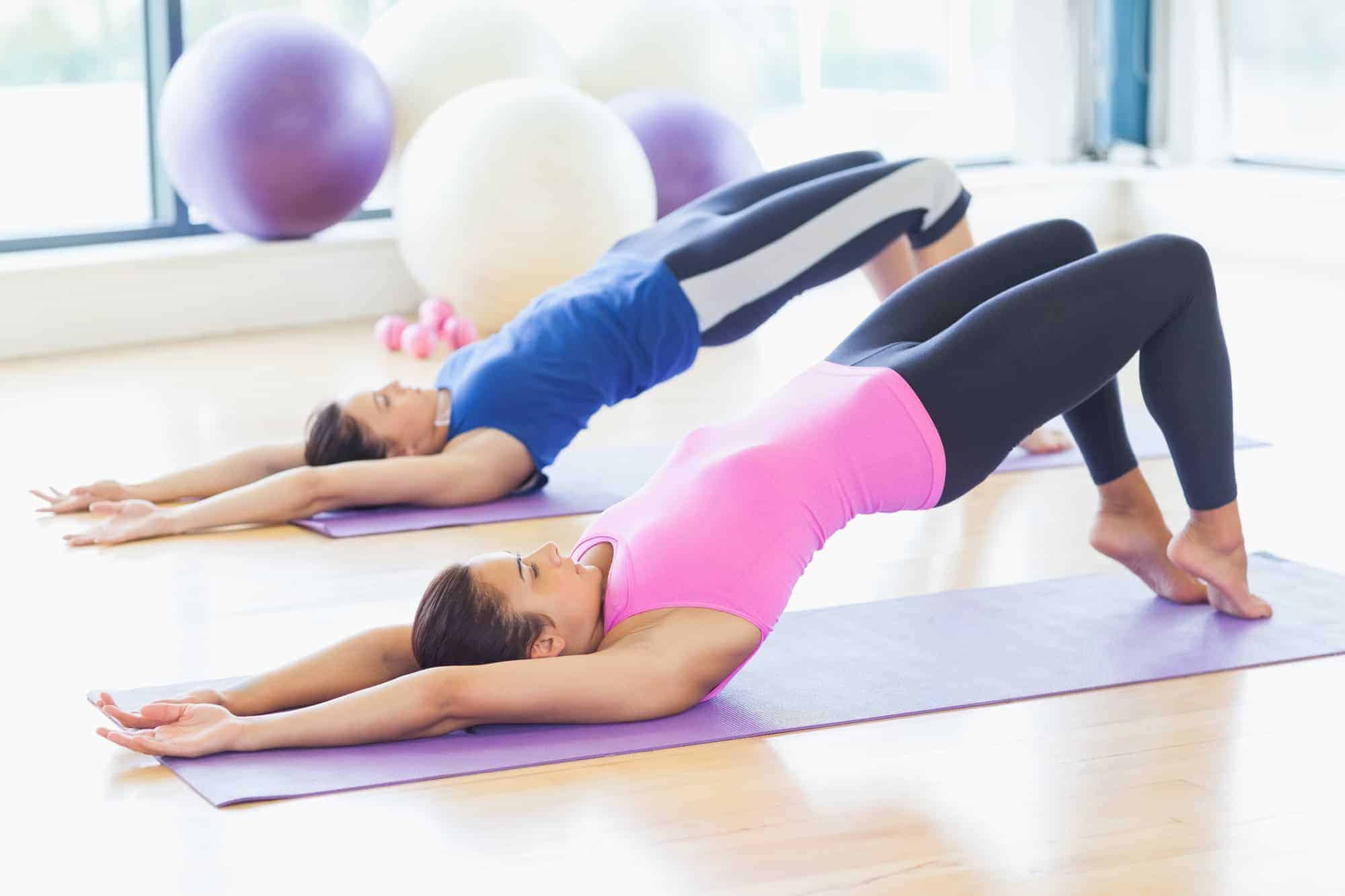
- Diabetic Foot Exercises: Exercises designed to increase blood flow to the feet and improve strength and flexibility can help manage diabetic foot disease and prevent complications.
Surgical Treatment Options:
- Surgical Debridement: In severe cases, debridement may be required to remove dead or infected tissue, helping to prevent the spread of infection and promote healing.
- Reconstructive Surgery: In cases of severe foot deformities or structural problems, surgery may be necessary to correct the foot’s alignment, improve function, and reduce the risk of further injury.
- Foot Amputation: In rare cases where infection or tissue damage is extensive and other treatments are ineffective, amputation may be required. However, this is considered a last resort.
Preventing Diabetic Foot Complications with Proper Orthopedic Care
Prevention is the key to avoiding serious complications related to diabetic foot disease. Proper foot care and regular check-ups with an orthopedic specialist can help prevent minor issues from becoming major problems.
- Daily Foot Care: Individuals with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, or redness. Regularly moisturizing the feet can help prevent dry, cracked skin, which can lead to infection.
- Regular Visits to an Orthopedic Specialist: Routine check-ups with an orthopedic or podiatric specialist allow for early detection of potential issues, such as changes in foot structure or the onset of ulcers.
- Lifestyle Changes: Proper blood sugar management is crucial for preventing diabetic foot disease. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and effective blood sugar control can significantly reduce the risk of developing foot complications.
Benefits of Early Orthopedic Intervention for Diabetic Foot Disease
The earlier orthopedic intervention is sought, the better the outcomes. Early diagnosis and treatment can:
- Prevent Further Complications: Timely intervention can prevent infections from spreading and reduce the risk of amputations.
- Enhance Mobility: Orthopedic treatments, such as custom footwear and exercises, can significantly improve comfort and mobility.
- Improve Recovery: With appropriate care, recovery times can be shortened, and the risk of long-term complications can be minimized.
By seeking early care, individuals with diabetes can maintain their independence and quality of life while avoiding serious foot-related issues.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease is essential for managing the complications that arise from diabetes, including infections, tissue damage, and mobility challenges. By seeking professional care early, individuals with diabetes can prevent further complications and improve their quality of life. If you or a loved one is experiencing foot problems related to diabetes, don’t hesitate to schedule a consultation with an orthopedic specialist to discuss treatment options and prevent further issues.