Lower back pain is a prevalent issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It can range from a mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain, interfering with everyday activities such as walking, sleeping, and working. Whether it’s caused by muscle strain, poor posture, or a chronic condition, lower back pain can have a significant impact on your quality of life. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available to alleviate pain and improve function. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes of lower back pain, treatment methods, and preventive measures to help you manage or eliminate discomfort and get back to your daily routine.
Understanding Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain refers to discomfort or pain in the lumbar region of the spine, which is located between the ribcage and pelvis. It is one of the most common complaints among adults and can affect people of all ages. The pain may be localized to the lower back or radiate to other areas, such as the legs, hips, or buttocks. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, degenerative conditions, and lifestyle habits.
Acute vs. Chronic Lower Back Pain: Lower back pain can be categorized into two main types: acute and chronic.
- Acute Lower Back Pain: This type of pain typically lasts a few days to a few weeks. It is often caused by sudden movements, such as lifting heavy objects, or by injuries like muscle strains. Acute pain may feel sharp and intense but usually resolves with proper rest and treatment.
- Chronic Lower Back Pain: Chronic pain lasts for 12 weeks or more, even after the initial injury or trigger has healed. This type of pain may be linked to long-term conditions such as degenerative disc disease, herniated discs, or sciatica. Managing chronic back pain often requires a multi-faceted approach, including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Common Causes of Lower Back Pain
Muscle Strain and Injury: One of the most common causes of lower back pain is muscle strain. Lifting heavy objects improperly, sudden twisting movements, or sitting in an awkward position for extended periods can cause muscle fibers to stretch or tear. This results in pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Poor posture and improper body mechanics when performing daily tasks can also contribute to muscle strain.
Herniated Disc and Sciatica: The spine consists of stacked vertebrae, and between each vertebra is a cushion-like structure called a disc. A herniated disc occurs when the gel-like center of the disc pushes through a tear in the outer ring, causing pressure on nearby nerves. This can lead to sharp pain, numbness, and tingling, especially in the legs—a condition known as sciatica. Sciatica can be particularly debilitating and requires prompt treatment.
Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the spinal discs naturally lose some of their flexibility, elasticity, and shock-absorbing ability. This condition, known as degenerative disc disease, can cause chronic lower back pain. The discs in the spine may become thinner, leading to increased friction and irritation between the vertebrae. This can result in dull, aching pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Other Conditions: Other less common conditions can also contribute to lower back pain, including:
- Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when a vertebra slips out of place, often putting pressure on the nerves.
- Spondylolysis: A defect or fracture in the vertebra that can cause pain and instability in the spine.
- Osteoarthritis: A condition that causes the cartilage in the joints to break down, leading to pain and stiffness in the lower back.
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain
At-Home Remedies: For many people, lower back pain can be managed effectively at home with simple remedies.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying an ice pack to the affected area during the first 48 hours can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain. After that, heat therapy (such as a warm compress or heating pad) can promote blood flow and relax muscles.
- Rest and Gentle Stretching: While complete bed rest is no longer recommended, taking short breaks to lie down in a comfortable position can alleviate pressure on the lower back. Gentle stretching exercises, such as knee-to-chest stretches, can improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking medication regularly.
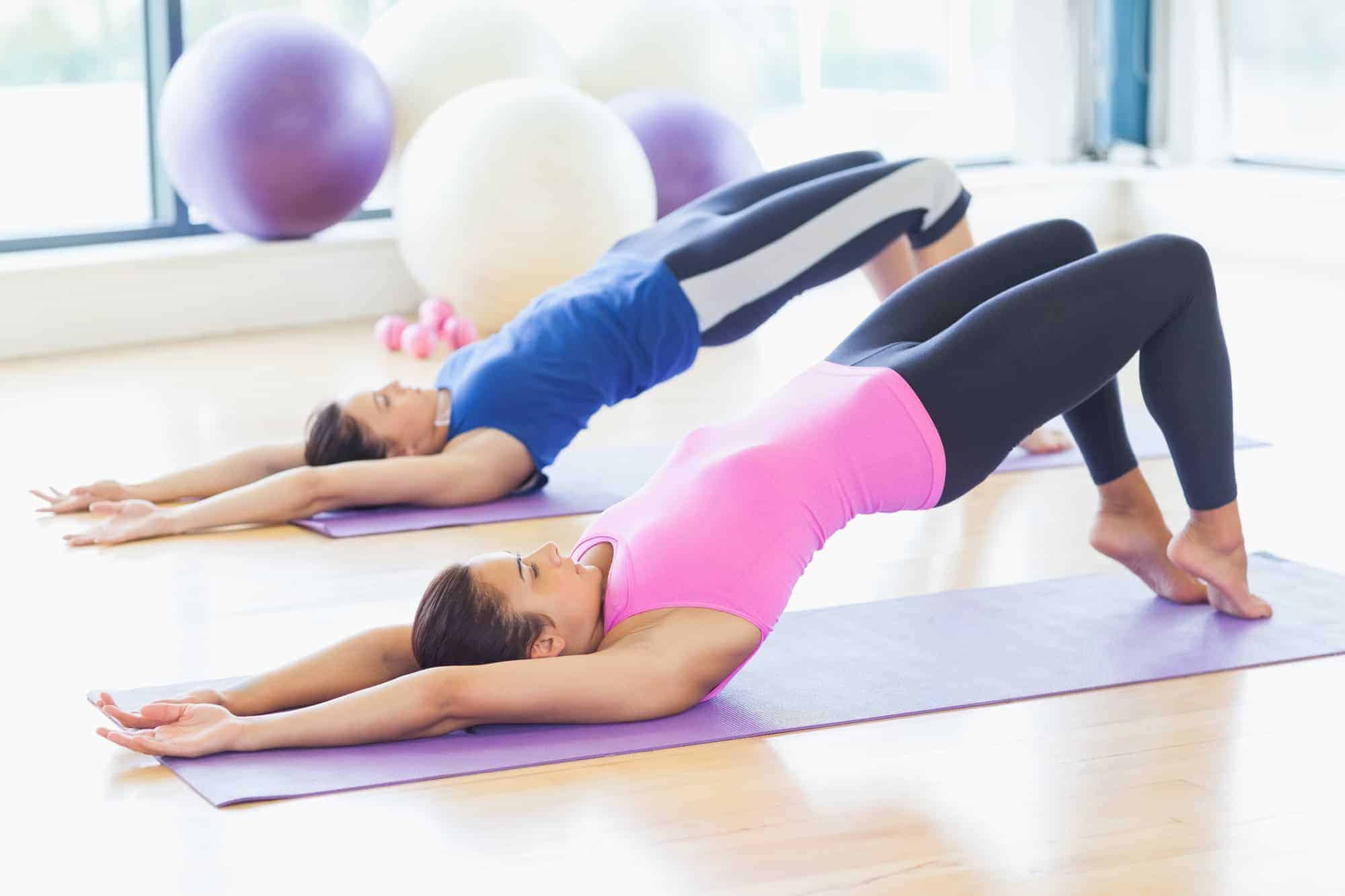
Physical Therapy and Exercises: Physical therapy is often recommended to treat lower back pain, especially for chronic cases. A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles that support the spine, improve posture, and increase flexibility. Some exercises may include:
- Core Strengthening: Strengthening the muscles of the abdomen, back, and pelvis helps support the spine and prevents future injuries.
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in the lower back.
- Posture Training: A physical therapist can teach you proper body mechanics to prevent further strain on your back.
Medications for Lower Back Pain: If over-the-counter medications do not provide sufficient relief, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
- Muscle Relaxants: These can help relieve muscle spasms and tightness in the back.
- Prescription NSAIDs: Stronger versions of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended for severe pain.
- Narcotic Pain Relievers: In cases of severe, short-term pain, your doctor may prescribe opioids. However, these are typically only used for a short duration due to the risk of dependency.
Alternative Treatments: For individuals seeking non-traditional approaches, several alternative treatments may help alleviate lower back pain.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors specialize in spinal manipulation, which can help restore alignment and reduce pain in the lower back.
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points of the body to stimulate healing and relieve pain.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help relax tense muscles, improve circulation, and reduce pain in the lower back.
Preventing Lower Back Pain
Ergonomics and Posture: Maintaining good posture and using proper ergonomics throughout the day can help prevent lower back pain. Here are a few tips:
- Sitting: Ensure that your workstation is set up to promote good posture. Sit with your feet flat on the floor, knees at a 90-degree angle, and your back supported by a chair with lumbar support.
- Standing: When standing, avoid slouching. Stand with your weight evenly distributed on both feet.
- Sleeping: Sleep on a firm mattress, and avoid sleeping on your stomach. Use a pillow to support your head and neck.
Strengthening Your Core and Lower Back Muscles: A strong core and lower back muscles are crucial for supporting the spine and preventing future injuries. Exercises such as planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts can help strengthen these muscles.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing lower back pain:
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, to keep your spine and muscles healthy.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the lower back, so maintaining a healthy body weight can reduce your risk of pain.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow to the spine, leading to weakened discs and increased pain.
When to Seek Medical Help
While most cases of Lower Back Pain Treatment improve with self-care and home treatment, there are times when professional help is necessary.
- Signs You Should See a Doctor: If the pain is severe, lasts more than a few weeks, or is accompanied by other symptoms like numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder control, it’s important to consult a doctor immediately.
- Diagnostic Tests: Your doctor may recommend imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to identify the cause of the pain. These tests help pinpoint issues like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or fractures.
Takeaway
Lower back pain is a common and often debilitating condition, but with the right treatment, it can be managed and even prevented. Whether you’re dealing with acute pain from a muscle strain or chronic pain due to degenerative conditions, there are a variety of effective treatments available. From at-home remedies like ice and heat therapy to professional treatments such as physical therapy and chiropractic care, finding the right approach is key to relieving your discomfort and improving your quality of life. Remember, if your pain persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical advice for a personalized treatment plan.