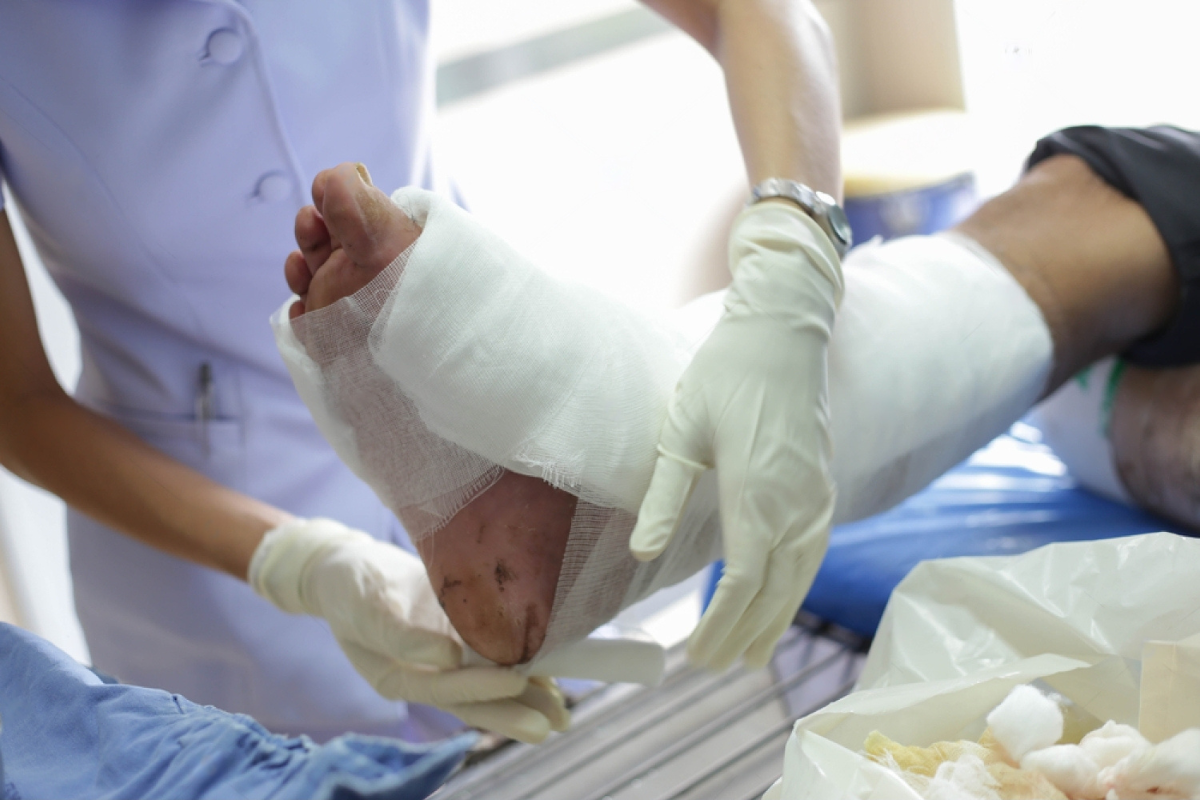
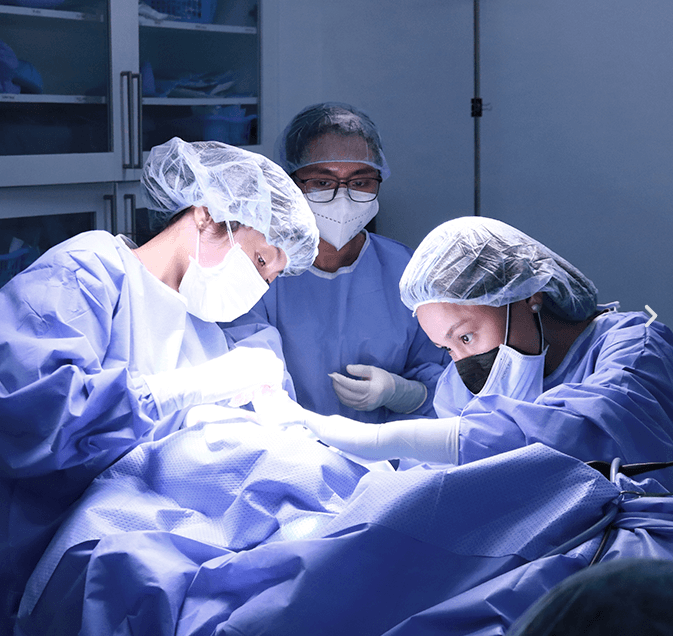
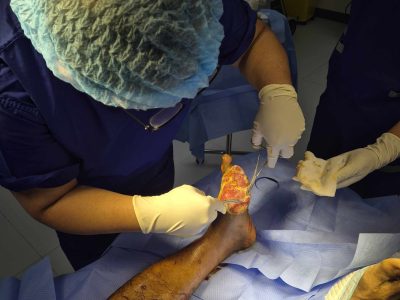
Effective management of infected wounds is crucial for ensuring proper healing and preserving mobility. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds plays a significant role in addressing complications arising from bacterial, fungal, or other pathogen-induced infections. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the nature of infected wounds, the importance of specialized orthopedic care, and the various treatment options available. By shedding light on these aspects, we hope to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your health.
Infected wounds present a significant challenge for many individuals, especially when complications extend to bones and surrounding tissues. The complexity of such infections requires an integrated approach that combines prompt medical attention with targeted orthopedic interventions. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is not only about eliminating infection but also about restoring function and preventing further complications. With increasing cases following injuries, surgeries, and chronic conditions, understanding the intricacies of this treatment modality becomes essential for patients, caregivers, and health professionals alike.
What Are Infected Wounds?
Defining Infected Wounds: Infected wounds occur when harmful pathogens—such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses—enter a break in the skin. This breach can result from a variety of causes including traumatic injuries, surgical incisions, or even chronic conditions that compromise the immune system. The introduction of pathogens into the wound site triggers an inflammatory response as the body attempts to fight off the infection.
Recognizing the Symptoms: Identifying an infected wound early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Swelling: The skin around the wound may become visibly red and swollen.
- Pain and Warmth: Increased pain or warmth around the affected area is often a sign of inflammation.
- Discharge or Pus: The presence of pus or other discharge indicates that the body is fighting off an infection.
- Fever and Malaise: In some cases, systemic signs such as fever or a general feeling of unwellness may occur, indicating that the infection is spreading.
Understanding these symptoms can guide timely intervention, ensuring that patients receive the necessary care before the infection exacerbates.
Causes of Infected Wounds: Several factors contribute to the development of infected wounds:
- Traumatic Injuries: Cuts, lacerations, or puncture wounds that occur in unsanitary conditions can easily become infected.
- Surgical Procedures: Postoperative wounds are at risk of infection, particularly if proper wound care protocols are not followed.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, vascular diseases, and immune system deficiencies can impair the body’s natural healing process, making infections more likely.
- Pressure Ulcers: Also known as bedsores, these can become infected if not managed with proper hygiene and care.
Why Orthopedic Care Is Essential for Infected Wounds
Preventing Complications: One of the primary concerns with infected wounds is the risk of complications. If left untreated, the infection can spread from the superficial layers of the skin to deeper tissues and even the bones—a condition known as osteomyelitis. Such infections can lead to irreversible tissue damage, impaired mobility, and in severe cases, amputation. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds focuses on preventing these complications by addressing the infection promptly and effectively.
Enhancing Healing and Mobility; Orthopedic specialists are trained to manage both the infection and the mechanical aspects of healing. By focusing on the structural integrity of bones and surrounding tissues, they ensure that the wound heals not only from an infectious standpoint but also in a manner that preserves function. This dual focus on infection control and rehabilitation is vital for restoring mobility and ensuring that patients can return to their daily activities with minimal disruption.
Comprehensive Approach to Care: The management of infected wounds often requires a multidisciplinary approach. While general physicians and infectious disease specialists play a role in antibiotic administration and infection control, orthopedic specialists provide the necessary surgical and non-surgical interventions. This collaboration ensures that all aspects of the wound are addressed, from eliminating the infection to rebuilding and reinforcing the affected tissues.
Orthopedic Treatments for Infected Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds encompasses a variety of interventions that can be categorized into medical treatments, surgical procedures, and supportive therapies.
Antibiotics and Medication: One of the cornerstones of treating infected wounds is the use of antibiotics. Depending on the severity and type of infection, doctors may prescribe:
- Oral Antibiotics: For milder infections, oral antibiotics can be sufficient in controlling bacterial growth.
- Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics: In more severe cases, IV antibiotics are administered to achieve higher concentrations of the medication in the bloodstream.
- Pain and Anti-inflammatory Medications: These help manage discomfort and reduce swelling, creating a better environment for healing.
The timely administration of these medications is crucial for preventing the spread of infection and setting the stage for further orthopedic interventions.
Wound Cleaning and Debridement
Wound debridement is the process of removing dead or infected tissue from the wound site. This procedure is essential for several reasons:
- Reduction of Bacterial Load: Removing necrotic tissue minimizes the environment in which bacteria can thrive.
- Promotion of Healing: By clearing out debris, healthy tissue can regenerate more effectively.
- Prevention of Further Complications: Proper cleaning reduces the risk of the infection spreading to deeper tissues and bones.
Surgical Interventions
Drainage and Abscess Management: For wounds that have developed abscesses, surgical drainage may be necessary. This involves creating an incision to allow pus to escape, thereby reducing the pressure and bacterial concentration in the area.
Advanced Debridement Techniques: In cases where the infection is severe, more extensive surgical debridement may be required. This not only involves removing infected tissue but also sometimes includes the removal of affected bone tissue to prevent the spread of osteomyelitis.
Reconstructive Procedures: Once the infection is under control, reconstructive procedures such as skin grafting or flap surgery might be performed to restore the appearance and function of the affected area. These procedures are essential for both cosmetic and functional recovery, particularly when significant tissue loss has occurred.
Supportive Therapies
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT, often known as vacuum-assisted closure, uses a controlled negative pressure environment to promote wound healing. This therapy helps reduce edema, increase blood flow, and draw the edges of the wound together, thereby accelerating the healing process.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): HBOT involves placing the patient in a pressurized chamber where they breathe pure oxygen. This treatment increases oxygen delivery to the wound, helping to kill bacteria and promote the growth of new tissue.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: After the infection is controlled and the wound has begun to heal, physical therapy is often recommended to restore mobility and strength. Orthopedic specialists work closely with physical therapists to design rehabilitation programs that ensure patients regain full function.
How to Prevent Wound Infections
Prevention is always preferable to treatment. Here are several strategies to reduce the risk of developing infected wounds:
Proper Wound Care and Hygiene
- Clean the Wound Thoroughly: Use mild soap and water to clean the wound immediately after an injury.
- Apply Antiseptics: Over-the-counter antiseptic solutions can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Cover the Wound: Keeping the wound covered with a sterile bandage helps protect it from external contaminants.
Regular Monitoring
Keep an eye on any wound for signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, minimizing the risk of complications.
Post-Surgical Care
Following surgery, adhere strictly to your doctor’s instructions regarding wound care. This may include regular cleaning, dressing changes, and avoiding activities that could stress the wound.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports the body’s natural healing processes.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking can impair circulation and delay wound healing.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining physical fitness can improve overall health and support recovery.
Finding the Right Orthopedic Specialist for Wound Care
Choosing the right healthcare provider is essential for effective treatment and recovery. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an orthopedic specialist for infected wound care:
Experience and Expertise: Look for a specialist with extensive experience in managing complex wound infections and orthopedic complications. Their background in both surgical and non-surgical treatments is crucial for comprehensive care.
Hospital Affiliation: Orthopedic specialists affiliated with reputable hospitals often have access to advanced diagnostic tools and state-of-the-art surgical facilities. This ensures that patients receive the highest quality care.
Treatment Options; Ensure that the specialist offers a full range of treatment options, from antibiotics and wound debridement to advanced surgical interventions and supportive therapies. This comprehensive approach is vital for addressing all aspects of the infection and healing process.
Reputation and Patient Reviews: Research patient testimonials and reviews to gauge the specialist’s effectiveness and bedside manner. Positive feedback and success stories can provide additional confidence in your choice.
Why Tec Orthopedics Stands Out: Tec Orthopedics is renowned for its expertise in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. With a multidisciplinary team and a patient-centered approach, they offer customized treatment plans designed to manage infections effectively while promoting optimal healing and recovery.
Takeaway
Effective management of infected wounds requires a multi-pronged approach that combines prompt medical intervention with specialized orthopedic care. By understanding the nature of infected wounds, recognizing the importance of early and effective treatment, and following preventive measures, patients can significantly improve their outcomes.
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is not merely about eradicating infection—it is about restoring function, preventing complications, and ensuring that every patient can return to a life of mobility and comfort. From medical therapies to advanced surgical procedures and supportive treatments like NPWT and HBOT, the comprehensive approach offered by specialized orthopedic care is indispensable.
If you or a loved one is facing the challenges of an infected wound, don’t wait until the condition worsens. Early intervention is key to preventing serious complications and ensuring a smoother, faster recovery. Reach out to a trusted orthopedic specialist, such as those at Tec Orthopedics, to discuss your symptoms and receive a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Empower yourself with the knowledge and resources necessary for effective wound management. Schedule a consultation today to explore how expert orthopedic treatment for infected wounds can pave the way toward a healthier, more active future.