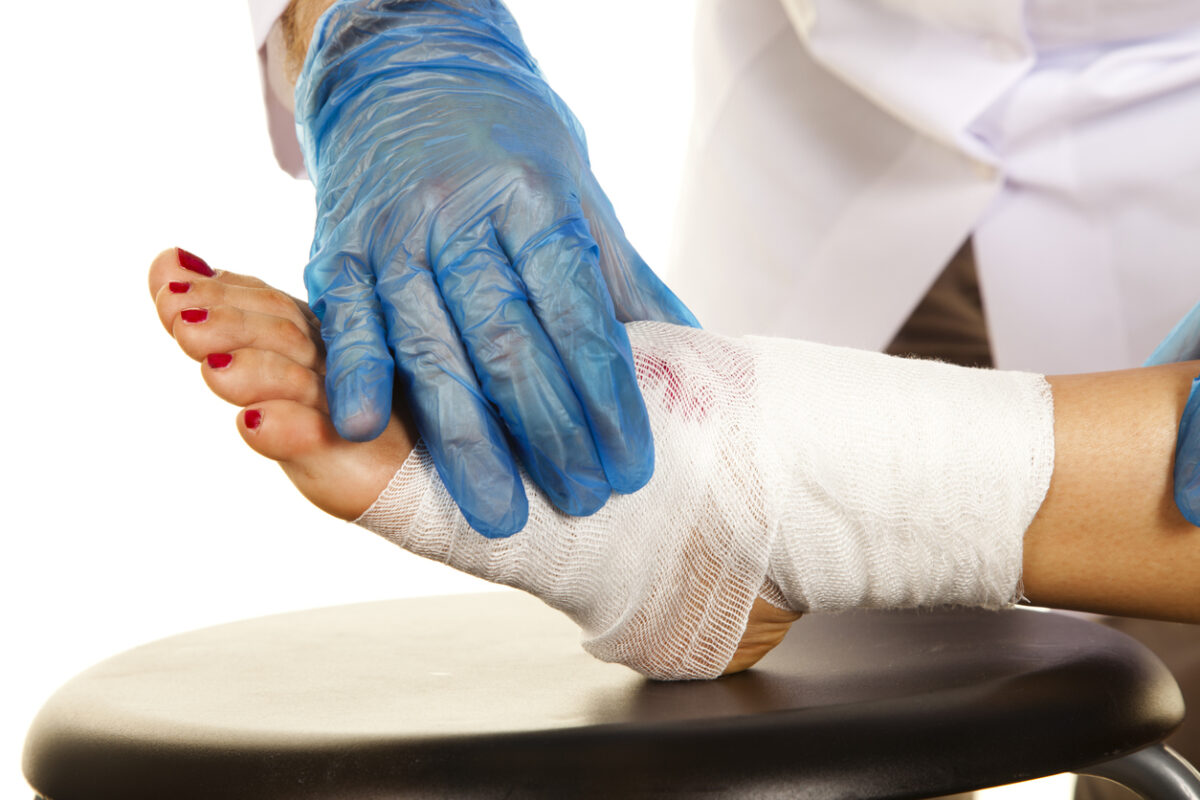
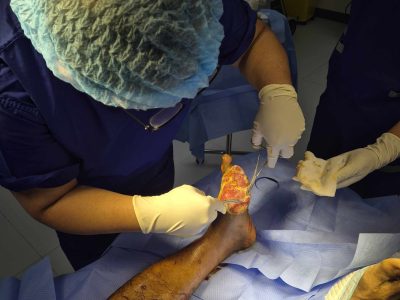
Diabetic foot complications demand prompt and specialized care to prevent severe outcomes. Foot ulcers are a common complication for those living with diabetes, often resulting from diminished circulation and nerve damage. Early and targeted orthopedic intervention plays a critical role in managing these ulcers, reducing the risk of infections, preserving healthy tissue, and restoring mobility.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetes can cause significant changes in the body, particularly affecting the feet. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to reduced blood flow and loss of sensation. Without proper feeling in the feet, small injuries may go unnoticed, potentially escalating into open wounds. Over time, poor circulation impedes the natural healing process, resulting in chronic ulcers.
Several factors contribute to the development of foot ulcers in diabetic patients:
- Neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves means that pain signals from the feet might not be recognized. This lack of feedback often leads to delayed treatment.
- Poor Circulation: Impaired blood flow reduces oxygen and essential nutrients needed for healing. This creates a vulnerable environment for bacteria, increasing the risk of infection.
- High Pressure Points: Repeated friction or pressure, especially for those with improperly fitted footwear, can cause skin breakdown, which may then evolve into an ulcer.
Understanding these underlying causes is crucial, as it highlights the necessity of a tailored orthopedic approach. The specialized care provided through Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Ulcers Caused by Diabetes is designed to address these complex issues, aiming to halt ulcer progression and avoid complications such as deep tissue infections or amputations.
The Orthopedic Approach to Treatment
Effective management of diabetic foot ulcers centers on three primary pillars: infection control, tissue preservation, and improved mobility. The orthopedic treatment strategy focuses on each of these areas with targeted interventions.
Infection Management: Foot ulcers in diabetic patients are highly susceptible to infections. The compromised blood flow not only hinders healing but also limits the delivery of antibiotics to the affected area. Orthopedic specialists utilize a combination of systemic antibiotic therapy and localized treatments to combat infection. Early intervention is vital, as untreated infections can lead to deeper tissue involvement or even systemic complications.
Tissue Preservation: The main goal of tissue preservation is to maintain as much healthy tissue as possible. Through meticulous debridement procedures—where dead or infected tissue is removed—orthopedic specialists create a cleaner wound environment that promotes healing. Preservation techniques also include the use of advanced wound dressings that support natural tissue repair while protecting the area from external contaminants.
Mobility Improvement: Limited mobility is a significant concern for diabetic patients suffering from foot ulcers. Pain, discomfort, and structural deformities often arise as the condition progresses. Orthopedic treatment plans are designed to restore mobility by reducing pain, realigning the foot structure, and providing supportive devices like custom orthotics. Improved mobility not only enhances quality of life but also reduces the risk of future ulcers by distributing pressure more evenly across the foot.
The comprehensive approach provided by Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Ulcers Caused by Diabetes underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary strategy. By addressing infection control, tissue preservation, and mobility improvement concurrently, healthcare professionals can optimize recovery outcomes and reduce long-term complications.
Treatment Techniques and Procedures
Several specialized procedures are integral to the orthopedic treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Each technique is selected based on the patient’s specific condition, ensuring a personalized treatment plan that maximizes recovery potential.
Debridement and Wound Cleaning: Debridement is the process of removing nonviable tissue from the ulcer. This step is critical to prevent the spread of infection and to stimulate the body’s natural healing response. Techniques vary from sharp debridement using surgical instruments to more conservative methods such as autolytic debridement, where dressings promote the body’s own enzymes to break down dead tissue.
Advanced Wound Dressings: Modern wound dressings provide an optimal healing environment by maintaining appropriate moisture levels and protecting the wound from external bacteria. These dressings often incorporate antimicrobial agents and are designed to be changed at intervals that support gradual tissue recovery. In many cases, the use of bioengineered skin substitutes or growth factors can further enhance tissue repair.
Offloading and Pressure Redistribution: Reducing pressure on the affected foot is a fundamental part of treatment. Offloading techniques involve using specialized footwear, custom orthotics, or even temporary immobilization devices. By redistributing weight away from the ulcerated area, these devices help reduce further trauma, allowing the tissue to heal effectively.
Surgical Interventions: For more severe cases, surgical procedures may be necessary. These interventions can include revascularization procedures to improve blood flow, corrective surgeries to realign foot structures, or in extreme cases, partial amputation to prevent the spread of infection. Each surgical decision is made after careful evaluation, ensuring that the benefits outweigh the risks.
Integration of Technology: Recent advancements in medical technology have improved the outcomes of orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot ulcers. Innovations such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) assist in reducing edema and promoting granulation tissue formation. Additionally, imaging techniques allow for precise mapping of tissue damage, guiding more targeted and effective treatments.
Patient Success Stories and Case Studies
Real-life examples underscore the effectiveness of Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Ulcers Caused by Diabetes. Consider a patient who experienced recurrent foot ulcers due to long-standing diabetes. Before seeking orthopedic care, the patient struggled with frequent infections and debilitating pain that significantly impacted daily activities.
Upon evaluation, a comprehensive treatment plan was devised that included aggressive debridement, the use of advanced antimicrobial dressings, and custom orthotics to redistribute foot pressure. Over several months, regular follow-up appointments confirmed gradual healing of the ulcer. Not only did the infection resolve, but the patient also experienced improved mobility, leading to a renewed sense of independence.
Another case involved a patient with a deep ulcer that had begun to affect surrounding tissues. The orthopedic team employed a combination of surgical intervention and non-surgical treatments to restore proper blood flow and remove necrotic tissue. With an emphasis on meticulous wound care and rehabilitation exercises, the patient’s recovery was notable, ultimately resulting in significant improvements in both function and quality of life.
These success stories highlight the tangible benefits of a coordinated orthopedic approach. By addressing the multifaceted challenges of diabetic foot ulcers, patients not only heal faster but also regain the confidence to lead more active lives.
Practical Foot Care and Prevention Tips for Diabetic Patients
Preventing foot ulcers is a critical component of overall diabetic care. A proactive approach can minimize the risk of complications and support long-term health. Here are some practical tips:
- Daily Inspection: Regularly check your feet for any signs of redness, blisters, or cuts. Early detection is key to preventing ulcers from developing.
- Proper Hygiene: Clean your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Ensure that you dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
- Moisturization: Use a suitable moisturizer to keep the skin soft and prevent cracking. Avoid applying moisturizer between the toes to reduce the risk of fungal infections.
- Appropriate Footwear: Invest in shoes that fit well and offer adequate support. Custom orthotics can also help distribute pressure evenly and reduce the risk of ulcer formation.
- Routine Medical Check-ups: Regular visits to a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist can help monitor foot health and catch potential issues before they escalate.
- Exercise and Mobility: Gentle exercises that promote circulation can be beneficial. However, consult with your healthcare provider to design a routine that doesn’t strain your feet.
Taking proactive steps not only prevents the development of foot ulcers but also supports overall well-being. Consistent foot care, combined with professional oversight, significantly reduces the likelihood of complications arising from diabetes.
Takeaway
Managing diabetic foot complications requires a comprehensive and personalized approach. Orthopedic Treatment for Foot Ulcers Caused by Diabetes offers a targeted solution, emphasizing infection control, tissue preservation, and improved mobility. By integrating advanced treatment techniques, personalized care plans, and preventive strategies, orthopedic specialists can help patients overcome the challenges posed by diabetic foot ulcers.
The journey to recovery begins with early detection and timely intervention. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms related to diabetic foot ulcers, it is essential to seek professional evaluation as soon as possible. The expertise provided by orthopedic specialists can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications and improve overall quality of life.
Your health is a priority. Consider scheduling an appointment with a trusted orthopedic provider to explore treatment options tailored to your specific needs. With dedicated care and proactive management, it is possible to navigate the challenges of diabetic foot ulcers and move toward a future of enhanced mobility and well-being.