Diabetic foot complications demand timely and targeted care, and specialized orthopedic treatment plays a crucial role in managing these issues. Foot ulcers in patients with diabetes can quickly become severe if not treated promptly, leading to infections, tissue damage, and reduced mobility. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding diabetic foot complications and the benefits of expert orthopedic intervention, with a focus on preventing complications and promoting healing.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Disease
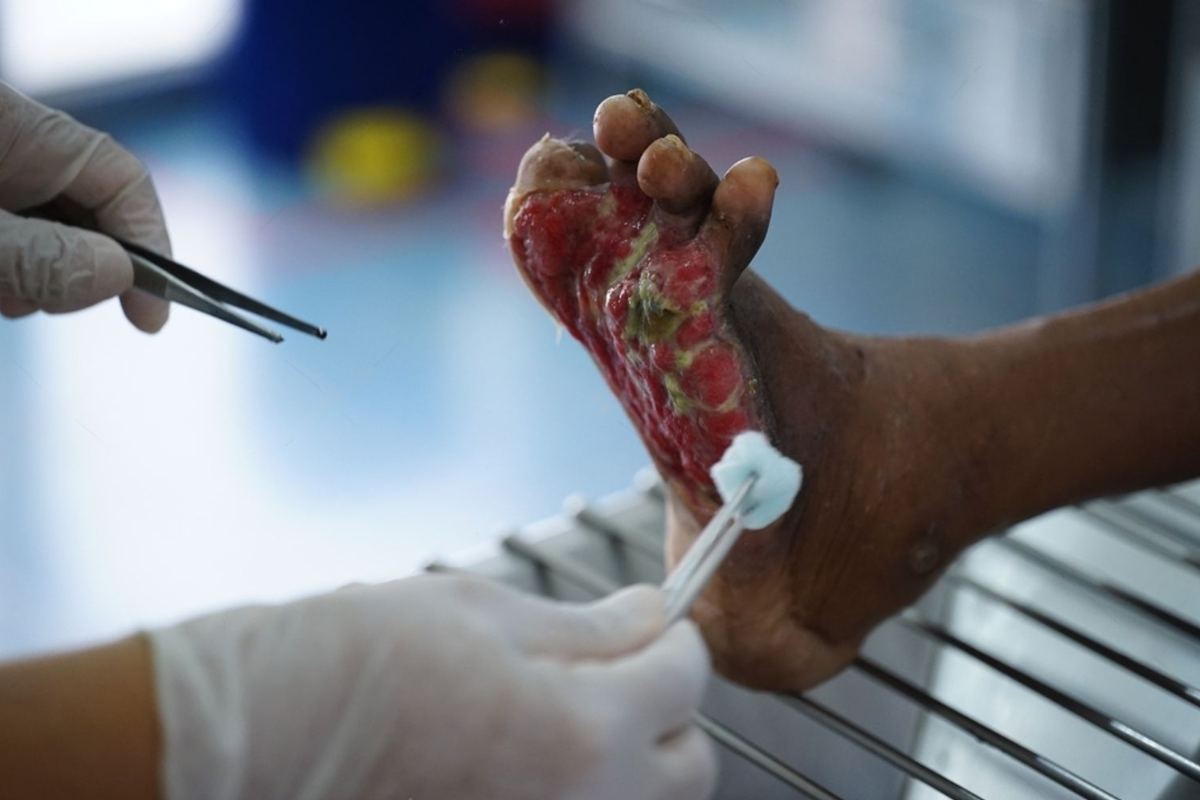
Diabetic foot disease is a common complication among individuals with diabetes, typically resulting from a combination of poor circulation and nerve damage. Reduced blood flow hinders the body’s ability to repair tissues, while neuropathy decreases the sensation in the feet, making injuries or sores less noticeable. Such conditions often lead to the development of chronic ulcers that, if unchecked, can progress into serious infections. Recognizing the early signs of diabetic foot issues is essential in preventing further deterioration.
Key characteristics of diabetic foot disease include:
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes can cause blood vessels to narrow, reducing oxygen and nutrient supply to the foot tissues.
- Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves diminishes sensation, meaning injuries can go unnoticed until they worsen.
- Chronic Ulcers: Even minor cuts or blisters can become open wounds, which may not heal due to compromised blood flow.
- Risk of Infection: Without proper care, these ulcers can lead to infections that may necessitate more extensive medical intervention, including surgery.
Causes and Risks Associated with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The roots of diabetic foot ulcers are complex and multifaceted. Poor blood circulation and neuropathy are among the chief culprits; however, several other factors contribute to the risk. Minor injuries, inappropriate footwear, and chronic high blood sugar levels all play a part in the onset of foot ulcers. When injuries go unnoticed or untreated due to reduced sensation, infections can develop and swiftly worsen the condition.
Risk factors include:
- Peripheral Vascular Disease: Reduced blood flow to the extremities leaves the feet vulnerable.
- Long-Standing Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing complications.
- Impaired Immune Response: High blood sugar levels can compromise the immune system, making the body less efficient at fighting off infections.
- Neglected Foot Care: Lack of regular inspection and care of the feet can allow even small wounds to become infected.
Awareness of these risk factors is critical for both patients and caregivers. Early detection and prompt intervention can significantly reduce the likelihood of complications and preserve quality of life.
The Role of Orthopedic Treatment in Managing Diabetic Foot Disease
Specialized care for foot ulcers, particularly among diabetes patients, often requires a dedicated orthopedic approach. The primary goal of orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease is to manage the condition before it leads to severe complications. Expert care focuses on a few main strategies:
- Infection Management: Prompt and effective control of infections is vital. Orthopedic specialists use a combination of antibiotics, wound debridement, and sometimes surgical interventions to clean and stabilize affected areas.
- Tissue Preservation: In efforts to maintain as much of the natural foot structure as possible, treatments focus on preserving healthy tissue. Careful monitoring and minimally invasive techniques help limit unnecessary tissue removal.
- Mobility Improvement: Rehabilitation and proper supportive care are crucial for restoring movement. Treatments may include physical therapy, custom orthotic devices, and walking aids to help patients regain strength and balance.
These strategies are not just about treating existing ulcers; they also aim to prevent further damage. By integrating diagnostic tests, advanced imaging, and careful evaluation, orthopedic treatment helps tailor interventions to each patient’s specific needs, thereby avoiding complications like amputations.
A Comprehensive Look at Orthopedic Care Procedures
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease starts with a thorough diagnosis to understand the severity of the condition. This typically involves various diagnostic tools:
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds help in assessing bone and soft tissue damage.
- Lab Tests: Blood work and wound cultures can detect infections and monitor overall health indicators.
- Physical Examinations: Detailed examinations help evaluate sensory loss, blood flow issues, and other complications.
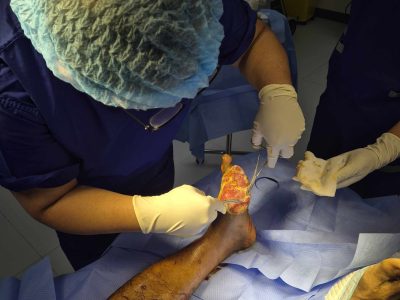
Following diagnosis, treatment protocols are designed to target the infection, remove necrotic tissue, and support healing. Some common procedures include:
- Debridement: Surgical or non-surgical removal of dead tissue to promote wound healing.
- Off-loading Techniques: Using specialized footwear or orthotic devices to reduce pressure on the affected area.
- Reconstructive Techniques: In cases where significant tissue damage has occurred, reconstructive surgery helps restore foot structure and function.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Timely administration of antibiotics is essential to combat bacterial infections and prevent sepsis.
These procedures are carefully chosen to cater to the unique challenges posed by diabetic foot ulcers. A well-planned treatment approach not only addresses the immediate concerns but also sets the stage for long-term recovery and improved mobility.
Enhancing Mobility and Quality of Life
Loss of mobility is a common consequence of diabetic foot disease, leading to a reduced quality of life. Orthopedic specialists work closely with physical therapists and rehabilitation experts to help patients regain their independence. Improving mobility involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises help strengthen muscles, enhance balance, and improve overall walking stability.
- Proper Footwear and Orthotic Devices: These are crucial for reducing pressure on the ulcerated area and promoting better movement.
- Regular Monitoring and Follow-Ups: Ongoing care ensures that any emerging issues are addressed quickly before they develop into more serious complications.
- Patient Education: Empowering patients with knowledge about proper foot care can lead to better daily practices, reducing the risk of future ulcers.
Investing in a comprehensive rehabilitation program is key to preserving overall mobility. The right blend of treatments and preventive strategies can make a significant difference in how patients manage their condition over time, helping them achieve a level of independence and improved quality of life.
Preventative Measures for Diabetic Foot Health
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when managing a condition as delicate as diabetic foot disease. Regular preventative measures can greatly reduce the risk of developing foot ulcers. Some essential preventative strategies include:
- Daily Foot Examinations: Checking for any signs of injury, redness, or swelling can help catch problems early.
- Proper Foot Hygiene: Washing and thoroughly drying the feet, particularly between the toes, reduces the risk of infection.
- Appropriate Footwear: Choosing shoes that fit well and offer adequate support can minimize the risk of cuts and blisters.
- Diabetes Management: Keeping blood sugar levels in control reduces the likelihood of developing complications related to poor circulation and neuropathy.
- Regular Medical Appointments: Routine check-ups with healthcare providers who specialize in diabetic foot care can catch issues before they escalate.
These measures not only help in reducing the occurrence of diabetic foot ulcers but also improve the overall health of the feet, lessening the burden on the orthopedic treatment process.
Selecting the Right Healthcare Provider
When it comes to managing diabetic foot complications, choosing the right orthopedic specialist is of utmost importance. Here are several factors to consider during the selection process:
- Credentials and Experience: Look for providers with specialized training and a track record in diabetic foot care and orthopedic treatment.
- Patient Testimonials: Reviews from previous patients can offer insight into the quality of care and success rates of the treatment.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: The best care often involves a team of experts including orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and rehabilitation therapists.
- Advanced Diagnostic and Treatment Facilities: Ensure the provider offers comprehensive diagnostics, from advanced imaging to effective antibiotic administration.
By choosing a provider experienced in delivering personalized care, patients can receive more efficient treatment, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring a smoother recovery process.
Takeaway
Effective management of diabetic foot complications requires a dedicated approach where early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and specialized treatment come together. Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease offers a powerful method to control infections, preserve tissue, and restore mobility. The integration of advanced procedures with a thorough preventative strategy enables patients to maintain their independence and improve their overall quality of life.
If you or a loved one is facing challenges with diabetic foot complications, consider seeking advice from a dedicated orthopedic specialist. Prompt consultation and a personalized treatment plan can significantly improve outcomes. Don’t wait until minor issues escalate; act early to protect your mobility and long-term health.