Understanding Non-Healing Wounds and Why They Matter
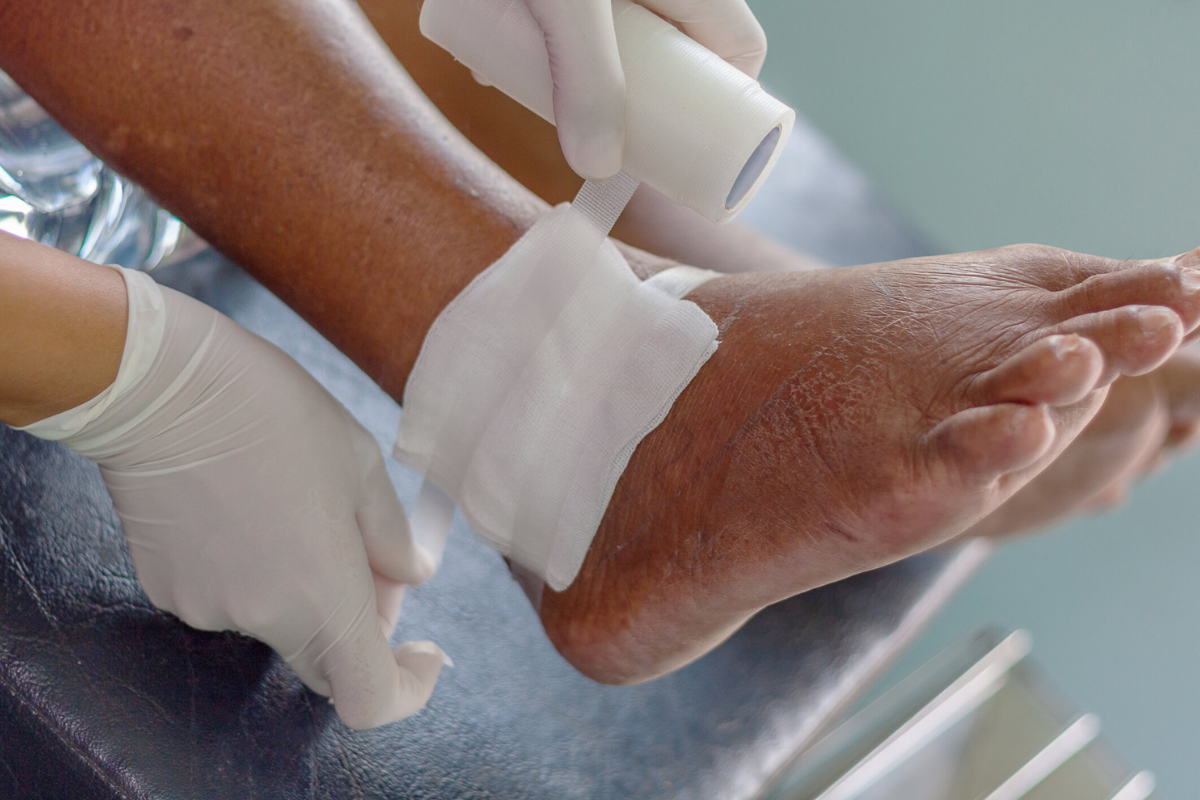
Non-healing wounds are a serious medical concern that extends beyond discomfort and inconvenience. Unlike typical wounds that progress through predictable stages of healing, non-healing wounds remain stagnant for weeks or even months without improvement. They are often linked to underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, vascular disease, infections, or poor circulation, making them complex and difficult to treat. When the healing process is stalled, patients face an increased risk of infections that can spread deeper into tissues and bones. This can lead to further complications, including hospitalization or even amputation in severe cases. Beyond physical health, these wounds can significantly affect quality of life by reducing mobility, independence, and emotional well-being. Understanding why wounds fail to heal is the first step in seeking the right kind of medical attention, particularly orthopedic treatment, which directly addresses the bone and joint structures often affected by chronic wounds.
The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Treating Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic specialists play a vital role when wounds fail to heal, especially when bone, joint, or soft tissue complications are present. Unlike general wound care providers, orthopedic doctors are trained to diagnose and treat issues related to musculoskeletal structures, which are often at the root of persistent wound problems. They are skilled at identifying whether conditions such as bone infections, structural deformities, or pressure points caused by poor biomechanics are interfering with healing. Collaboration is also a key part of orthopedic care. Orthopedic specialists often work with vascular surgeons, podiatrists, and wound care teams to provide a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of healing. Patients who delay seeking orthopedic evaluation may allow the problem to progress to the point of severe infection or tissue damage, reducing treatment options. For this reason, early intervention from an orthopedic doctor is critical to improving outcomes for non-healing wounds.
Common Types of Non-Healing Wounds Requiring Orthopedic Care
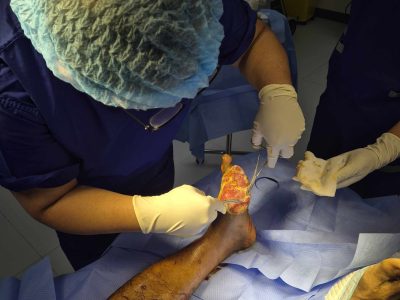
Certain types of wounds are especially prone to needing orthopedic involvement. Diabetic foot ulcers, for example, often extend to the bone and are complicated by poor blood flow and nerve damage. Pressure sores, also known as bedsores, frequently affect immobile patients and may expose joints or bones if left untreated. Traumatic injuries such as compound fractures or crush injuries may heal slowly when bone alignment is poor or infection sets in. Post-surgical complications are another category that requires orthopedic expertise, as surgical wounds near joints can break down or become infected. Chronic osteomyelitis, a deep-seated bone infection, is one of the most severe conditions associated with non-healing wounds and demands highly specialized orthopedic treatment. Each of these wound types requires a tailored approach, as the strategies for managing diabetic ulcers differ from those for traumatic injuries or surgical site infections. The common thread is the need for orthopedic insight when musculoskeletal structures are directly or indirectly involved.
Orthopedic Diagnostic Approaches for Non-Healing Wounds
Effective treatment begins with accurate diagnosis, and orthopedic specialists rely on a wide range of diagnostic tools to uncover the root cause of non-healing wounds. Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans provide detailed views of bone health, detecting infections, fractures, or deformities that may be impeding recovery. Laboratory tests, including cultures and blood work, are crucial for identifying bacterial infections or poor circulation issues. A biomechanical assessment may also be performed to evaluate gait, posture, or pressure points that worsen wounds, particularly in the feet and legs. Orthopedic doctors also examine whether underlying conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, or osteoporosis are contributing factors. By combining these diagnostic techniques, they can pinpoint not just the surface problem but the structural or systemic reasons behind delayed healing. This thorough evaluation ensures that treatment addresses the wound comprehensively rather than focusing only on the visible damage.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatment Options for Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds encompasses a range of advanced interventions designed to restore healing and prevent complications. Surgical options often include debridement, which removes dead or infected tissue to promote new growth, or reconstructive procedures that rebuild damaged areas. In cases involving significant bone loss, bone grafting may be performed to restore stability and encourage healing. Orthopedic implants or external fixators are sometimes necessary to stabilize fractures or deformities, giving wounds the structural support needed to close properly. Beyond surgery, supportive treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy can enhance tissue repair by increasing oxygen supply to the wound site. Orthopedic specialists are also turning to innovative biologic therapies, including growth factors, skin substitutes, and regenerative medicine approaches, to accelerate recovery. Each of these treatments is selected based on the patient’s condition, wound severity, and overall health, ensuring a customized plan that maximizes the chances of healing.
The Importance of Rehabilitation in Orthopedic Wound Care
Rehabilitation is an often-overlooked component of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, yet it plays a pivotal role in long-term recovery. Physical therapy helps restore mobility and improve circulation, both of which are essential for healing. Exercises are carefully designed to avoid placing stress on the wound while gradually strengthening surrounding muscles and joints. Pressure offloading is another crucial aspect, particularly for wounds on the feet or legs, where specialized footwear, orthotic devices, or supportive braces reduce strain. Patients are also educated on proper wound care practices, dietary adjustments, and strategies to avoid recurrence. For individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, rehabilitation may involve lifestyle coaching and continuous monitoring to prevent complications. Rehabilitation not only promotes faster healing but also enhances overall quality of life by enabling patients to regain independence and confidence. Orthopedic care is most effective when rehabilitation is fully integrated into the treatment plan.
Preventing Non-Healing Wounds with Orthopedic Care
Prevention is just as important as treatment when it comes to managing chronic wounds. Orthopedic specialists emphasize early screening for high-risk patients, such as those with diabetes, vascular disease, or limited mobility. Regular monitoring allows potential issues to be detected before they progress into serious complications. Lifestyle changes, including weight management, exercise, and proper nutrition, can significantly reduce the risk of wounds failing to heal. Orthopedic doctors also stress the importance of footwear and assistive devices for patients prone to foot ulcers or pressure sores. Detecting infections early and treating them promptly is another key strategy for prevention. Routine follow-up appointments ensure that patients receive ongoing care, and adjustments to treatment plans can be made as needed. By addressing both immediate concerns and long-term risks, orthopedic specialists help patients avoid the devastating consequences of untreated non-healing wounds.
FAQ Section
Q1: What makes orthopedic treatment different from general wound care?
Orthopedic treatment focuses on the musculoskeletal system, addressing issues such as bone infections, fractures, and deformities that interfere with healing. General wound care often targets the surface of the wound, while orthopedic specialists deal with deeper complications involving bones and joints.
Q2: Can orthopedic surgery completely heal non-healing wounds?
In many cases, surgery can significantly improve healing by removing infected tissue, repairing bone damage, or reconstructing affected areas. However, complete healing depends on the patient’s overall health, the severity of the wound, and whether underlying conditions such as diabetes are controlled.
Q3: How do I know if my wound requires an orthopedic specialist?
If a wound persists for more than a few weeks without improvement, shows signs of infection, or is located near a bone or joint, it is advisable to seek orthopedic evaluation. Wounds that expose bone or are linked to traumatic injuries also require immediate orthopedic attention.
Q4: Are there non-surgical orthopedic treatments for slow-healing wounds?
Yes, non-surgical treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, biologic dressings, orthotic support, and physical rehabilitation can all support healing. The approach depends on the wound’s characteristics and the patient’s individual needs.
Q5: What are the risks of delaying orthopedic consultation for non-healing wounds?
Delaying care can lead to worsening infections, spreading to bones or joints, and potentially causing permanent disability. In severe cases, untreated non-healing wounds may result in amputation, highlighting the urgency of timely orthopedic treatment.