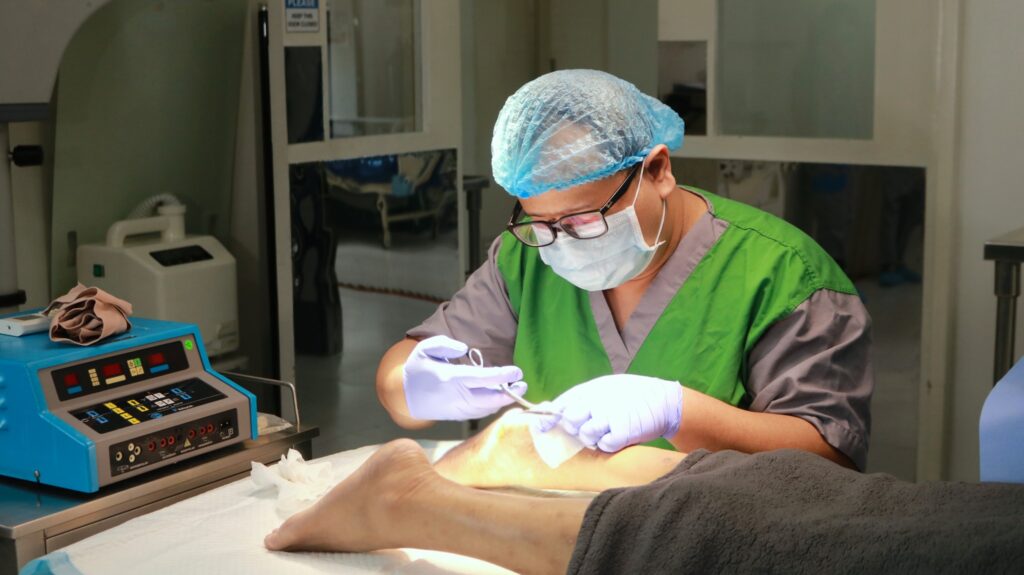
Wound Care Hospital Benefits for High-Risk Patients
Choosing the right wound care hospital can significantly impact the healing process and overall recovery experience. Wounds, whether chronic, post-surgical, or related to underlying health
Surgery is a branch of medicine that involves the treatment of injuries, diseases, and deformities through operative procedures. It is a vital medical intervention used to diagnose, treat, or manage a variety of conditions that cannot be addressed effectively with medication or other non-invasive therapies.
Modern surgery incorporates advanced techniques such as robotic-assisted systems, laser surgery, and precision-guided tools to enhance outcomes. Anesthesia and sterilization have revolutionized patient safety and comfort during procedures.
Post-surgical care is crucial for recovery, involving wound management, physical therapy, and regular follow-ups to monitor healing. Recovery times vary based on the type and complexity of the procedure.
Surgery continues to evolve with technological advancements, improving success rates and minimizing risks, making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare.

Choosing the right wound care hospital can significantly impact the healing process and overall recovery experience. Wounds, whether chronic, post-surgical, or related to underlying health

Living with joint pain, muscle strain, or limited mobility can affect every part of daily life. Whether it is difficulty performing routine tasks, chronic discomfort,
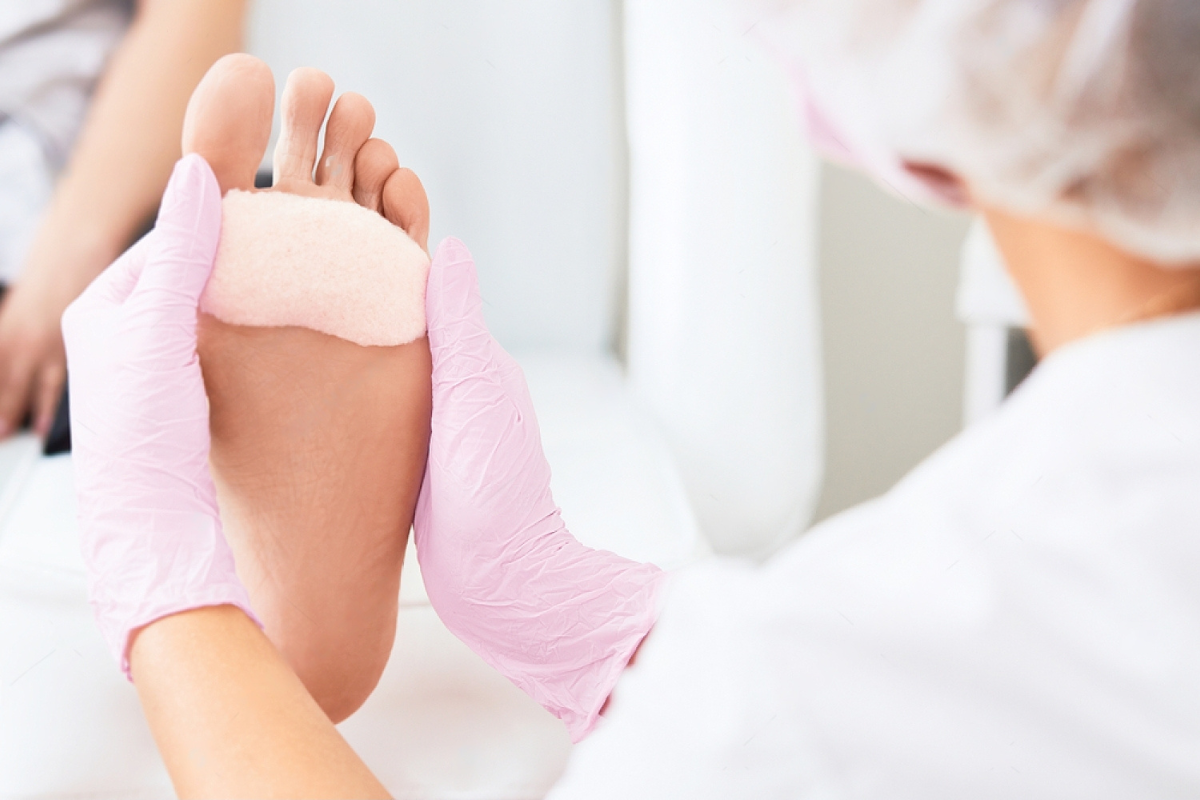
Toe ulcers are a serious health concern that can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. These open sores often result from poor circulation, nerve
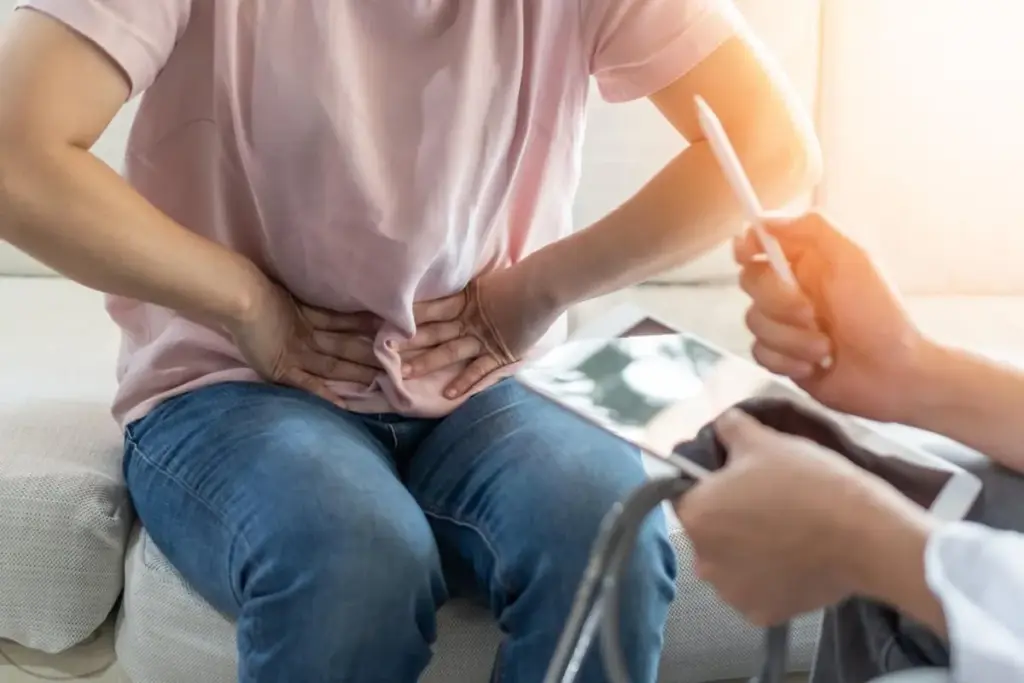

Understanding Varicocele and Why Removal Is Recommended Varicocele is a condition where veins inside the scrotum become enlarged due to improper blood flow. These veins
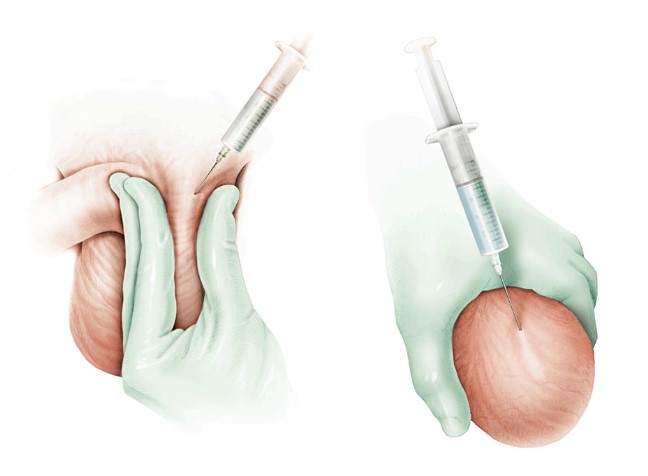
Hydrocele is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid around the testicle, leading to noticeable swelling in the scrotum. While often painless, it can
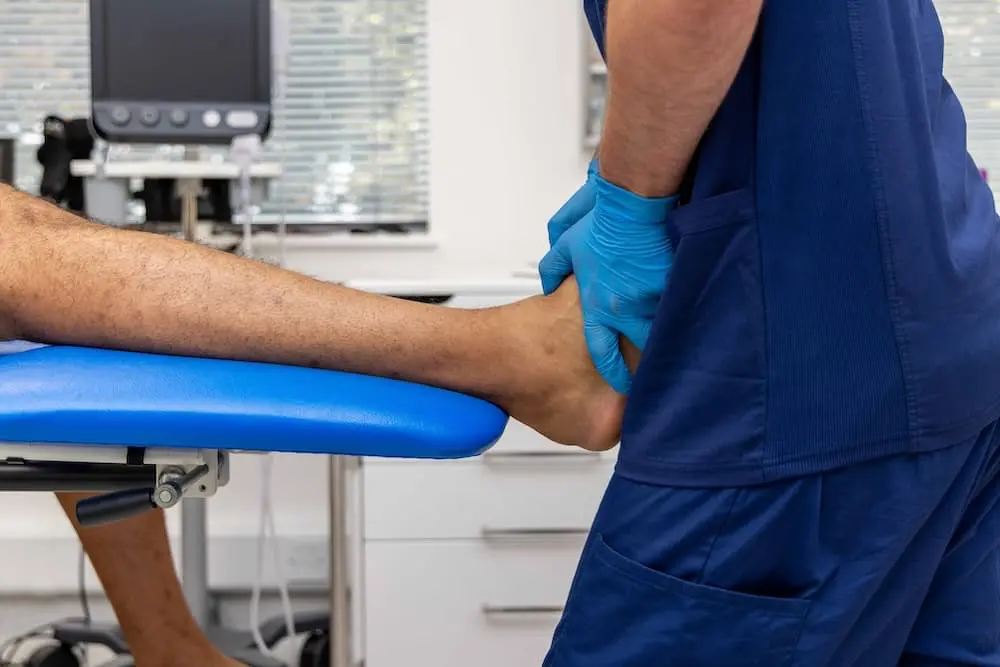
Foot injuries can affect mobility, balance, and daily activities, making even simple tasks painful. Common foot injuries include sprains, strains, fractures, plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis,